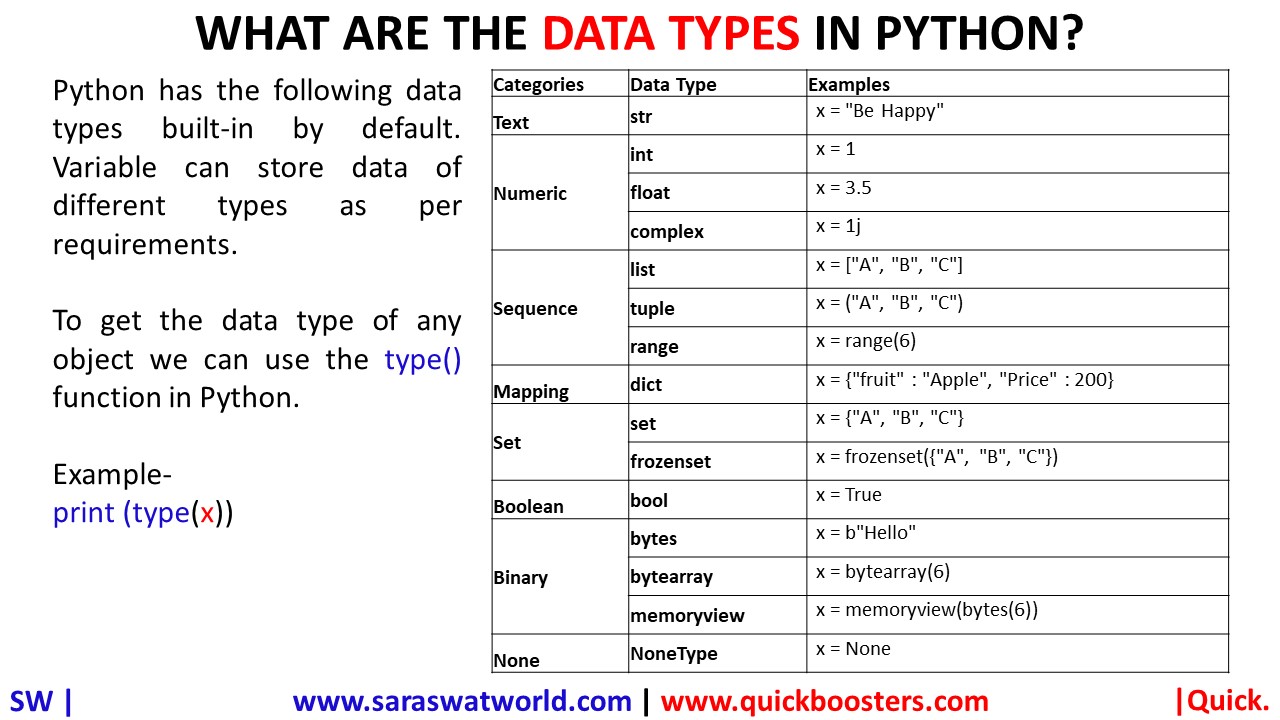
Python has the following data types built-in by default. Variable can store data of different types as per requirements.
| Categories | Data Type | Example |
| Text | str | x = “Be Happy” |
| Numeric | int | x = 1 |
| Numeric | float | x = 3.5 |
| Numeric | complex | x = 1j |
| Sequence | list | x = [“A”, “B”, “C”] |
| Sequence | tuple | x = (“A”, “B”, “C”) |
| Sequence | range | x = range(6) |
| Mapping | dict | x = {“fruit” : “Apple”, “Price” : 200} |
| Set | set | x = {“A”, “B”, “C”} |
| Set | frozenset | x = frozenset({“A”, “B”, “C”}) |
| Boolean | bool | x = True |
| Binary | bytes | x = b”Hello” |
| Binary | bytearray | x = bytearray(6) |
| Binary | memoryview | x = memoryview(bytes(6)) |
| None | NoneType | x = None |
To get the data type of any object we can use the type() function in Python.
Example-
print (type(x))
Python Collections (Arrays)
There are four collection data types in the Python programming language:
List
List is a collection which is ordered and changeable. Allows duplicate members.
Tuple
Tuple is a collection which is ordered and unchangeable. Allows duplicate members.
Set
Set is a collection which is unordered, unchangeable, and unindexed. No duplicate members.
Set items are unchangeable, but you can remove and/or add items.
Dictionary
is a collection which is ordered and changeable. No duplicate members.
Properties of collection datatypes in python
| Collection DataTypes | Ordered | Mutable-Changeable | Unique elements |
| List | Yes | Yes | No |
| Tuple | Yes | No | No |
| Set | No | No | Yes |
| Dictionary | Yes | Yes | Yes |