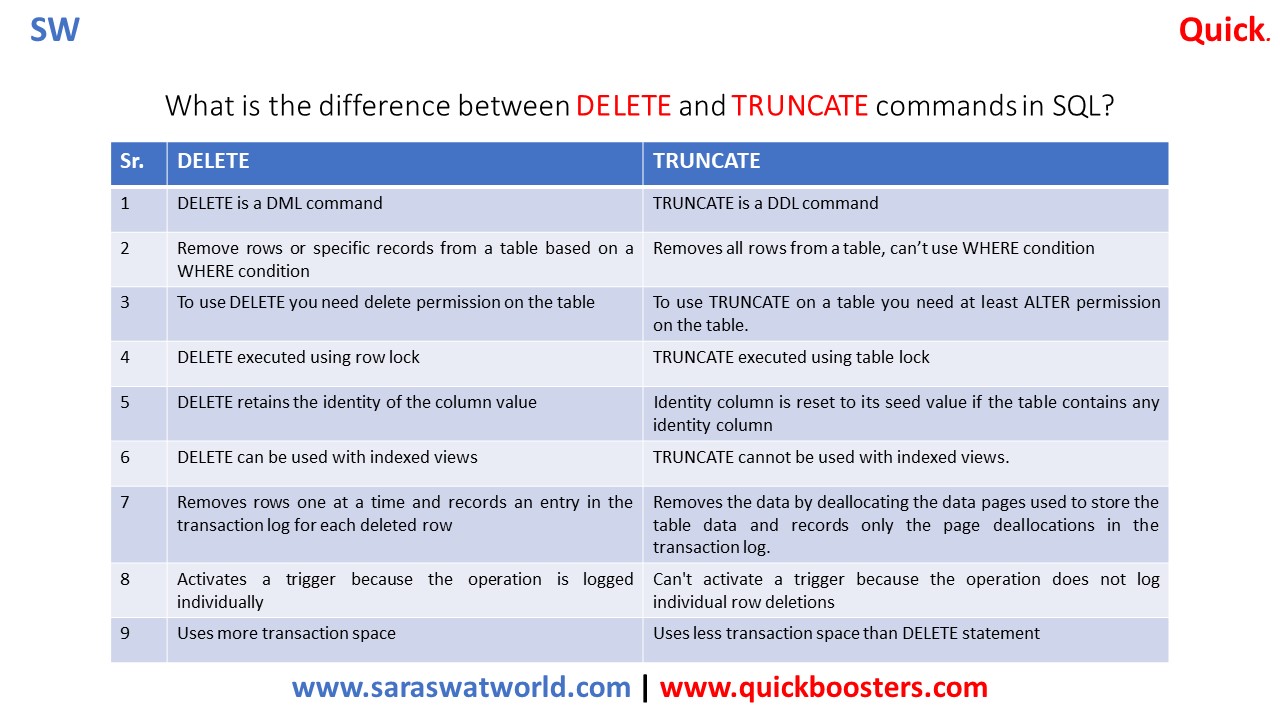
| Sr. | DELETE | TRUNCATE |
| 1 | DELETE is a DML command | TRUNCATE is a DDL command |
| 2 | Remove rows or specific records from a table based on a WHERE condition | Removes all rows from a table, can’t use WHERE condition |
| 3 | To use DELETE you need delete permission on the table | To use TRUNCATE on a table you need at least ALTER permission on the table. |
| 4 | DELETE executed using row lock | TRUNCATE executed using table lock |
| 5 | DELETE retains the identity of the column value | Identity column is reset to its seed value if the table contains any identity column |
| 6 | DELETE can be used with indexed views | TRUNCATE cannot be used with indexed views. |
| 7 | Delete removes rows one at a time and records an entry in the transaction log for each deleted row | TRUNCATE removes the data by deallocating the data pages used to store the table data and records only the page deallocations in the transaction log. |
| 8 | DELETE activates a trigger because the operation is logged individually | TRUNCATE can’t activate a trigger because the operation does not log individual row deletions |
| 9 | DELETE Uses more transaction space | TRUNCATE Uses less transaction space than DELETE statement |